For reporting purposes, ABC Inc. is willing to determine the net realizable value of the inventory that will be sold. CFI’s Reading Financial Statements course will go over how to read a company’s complete set of financial statements. We use the Net Realizable Value to account that assets are sometimes worth less than on paper. Take the inventory breakdown as of 31 December 2020 and calculate the Average Cost per item (End V / End Q). As our sales team offers discounts for various reasons, we also calculate the Net Sales for each item. Timely adjusting the values allows us to avoid carrying losses forward into future periods.
Net Realizable Value in Accounting
The firm remains concerned about evaluating the assets properly, which makes calculating NRV a conservative approach, indicating that the firm should not overstate the profit by showing a lesser value of its assets. Accounting conservatism is a principle that requires company accounts to be prepared with caution and high degrees of verification. These bookkeeping guidelines must be followed before a company can make a legal claim to any profit. The general concept is to factor in the worst-case scenario of a firm’s financial future.
Example NRV Analysis
- In effect, companies are prevented from overstating the value of their inventory, which reduces the risk of misleading investors.
- However, it is important to know the steps to follow to make an accurate calculation besides knowing the formula.
- NRV is particularly important for valuing inventory and accounts receivable.
- NRV is the valuation method which is adopted by the firms to ensure they price the assets properly.
- Magnimetrics and the author of this publication accept no responsibility for any damages or losses sustained as a result of using the information presented in the publication.
Since in NRV, a firm also considers the cost, hence it is known as a conservative approach to the transaction. In practice, the NRV method is most common in inventory accounting, as well as for calculating the value of accounts receivable (A/R). Companies must now use the lower cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules. Net realizable value of accounts receivable minus the credit balance give you the NRV, which can also be expressed as a debit balance in the asset account. Are you a business owner looking to complete the eventual sale of equipment or inventory?
- Now that you have access to both of the figures outlined above, it is time to deduce your selling cost or allowance for doubtful accounts from your expected selling price or FMV.
- We then calculate the average percentage of NRV Adjustment Value off of End Value (the value as of 31 December 2020).
- Our solution has the ability to prepare and post journal entries, which will be automatically posted into the ERP, automating 70% of your account reconciliation process.
- So the telephones’ NRV can be calculated as $5,000 – $240 -$40, which is equal to $4,720.
- By considering potential bad debts, NRV helps management make better decisions related to credit policies, collection efforts, and financial forecasting.
- The total production and selling costs are the expenses required to facilitate the trade.
Accountants and bookkeepers
It usually requires certified public accountants (CPAs) to do the job as it involves a lot of judgment. The net realizable value is an essential measure in inventory accounting under the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and the International Financing Reporting Standards (IFRS). The calculation net realizable value of NRV is critical because it prevents the overstatement of the assets’ valuation. The estimated NRV also reflects the specific purpose for which the inventory is kept. For instance, the NRV of inventory reserved for confirmed sales or service agreements is derived from the agreed contract price (IAS 2.31).
This means that you do not need to use a net realizable value calculator in order to gain access to this vital information. In fact, the net realizable value formula is divided into just three steps. In the following year, the market value of the green widget declines to $115. The cost is still $50, and the cost to prepare it for sale is $20, so the net realizable value is $45 ($115 market value – $50 cost – $20 completion cost). Since the net realizable value of $45 is lower than the cost of $50, ABC should record a loss of $5 on the inventory item, thereby reducing its recorded cost to $45.
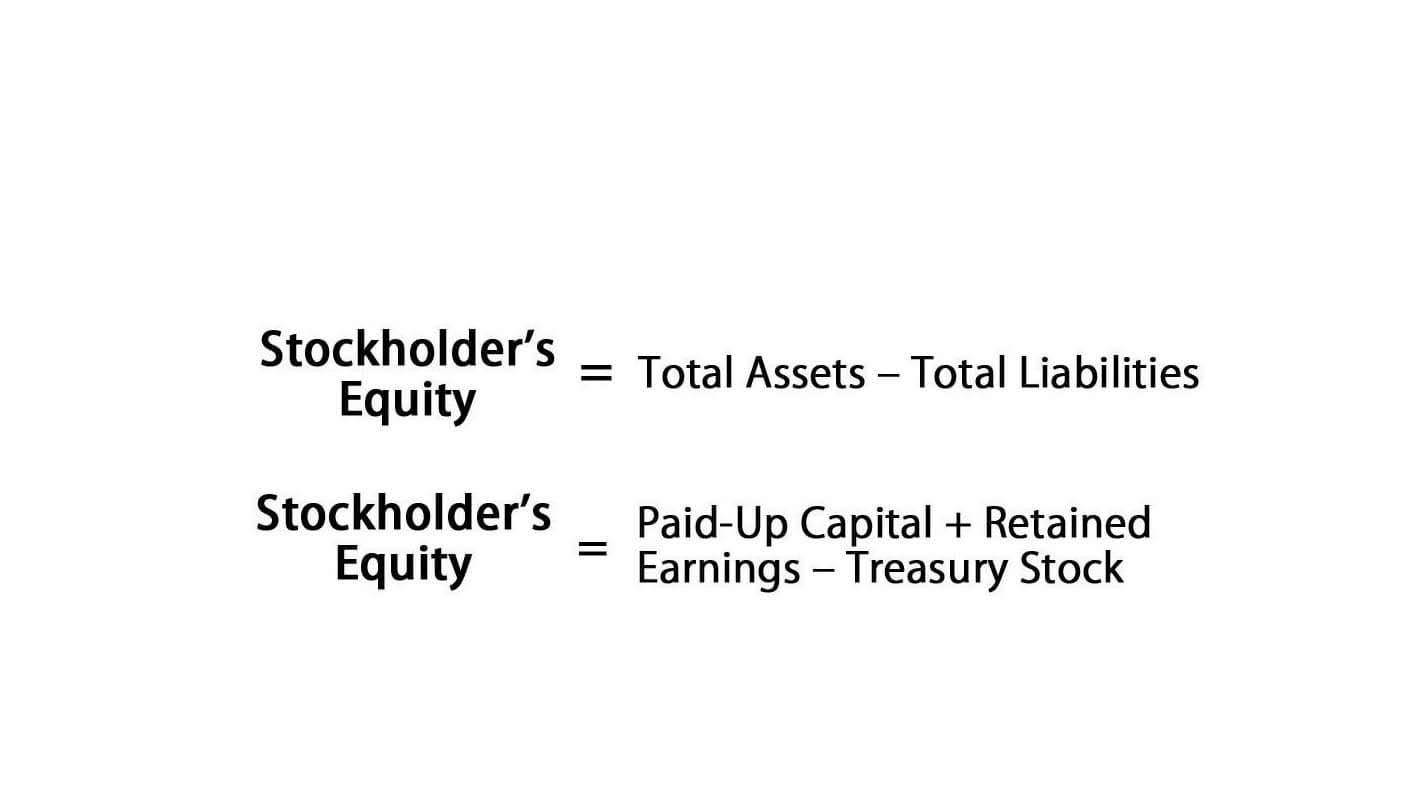
Understanding Net Realizable Value (NRV)
- As we usually perform such analysis later in the next year, let’s assume we are now at the end of Q1 of 2021.
- Therefore, the net realizable value (NRV) estimates the amount that a seller would expect to receive if the asset in question was sold, net of any selling or disposal costs.
- NRV ensures that assets on the balance sheet, specifically A/R, are not overstated.
- As technology evolves and production capabilities expand, unsold inventory items may quickly lose their luster and become obsolete.
- When it does so, it reports an expense for the amount added to the allowance.
- Despite its advantages, calculating NRV can be complex and time-consuming, requiring precise estimates and regular adjustments due to market fluctuations.
- This was updated in 2015 to where companies must now use the lower of cost or NRV method, which is more consistent with IFRS rules.
- To calculate your net realizable value, you must subtract the estimated cost of selling costs (the expenses incurred in making the asset market-ready, alongside product shipping or transportation cost) from its expected sale price.
- To calculate the Net Realizable Value, subtract the Cost of Goods Sold and the Estimated Selling Expenses from the Selling Price of the inventory.
- The NRV is commonly used in the estimation of the value of ending inventory or accounts receivable.
- To properly report the sale, Star Company is determining the net realizable value for the inventory they’re selling.
- However, this leads to a contracting economy that increases unemployment.